1. Identify the products and draw the curved-arrow mechanism for each of the following stereospecific E2 reaction: Drawing Newman projections to achieve the correct anti-periplanar conformation will be helpful. answer. This content is for registered users only.
Answered: Predict reagents needed to complete… | bartleby
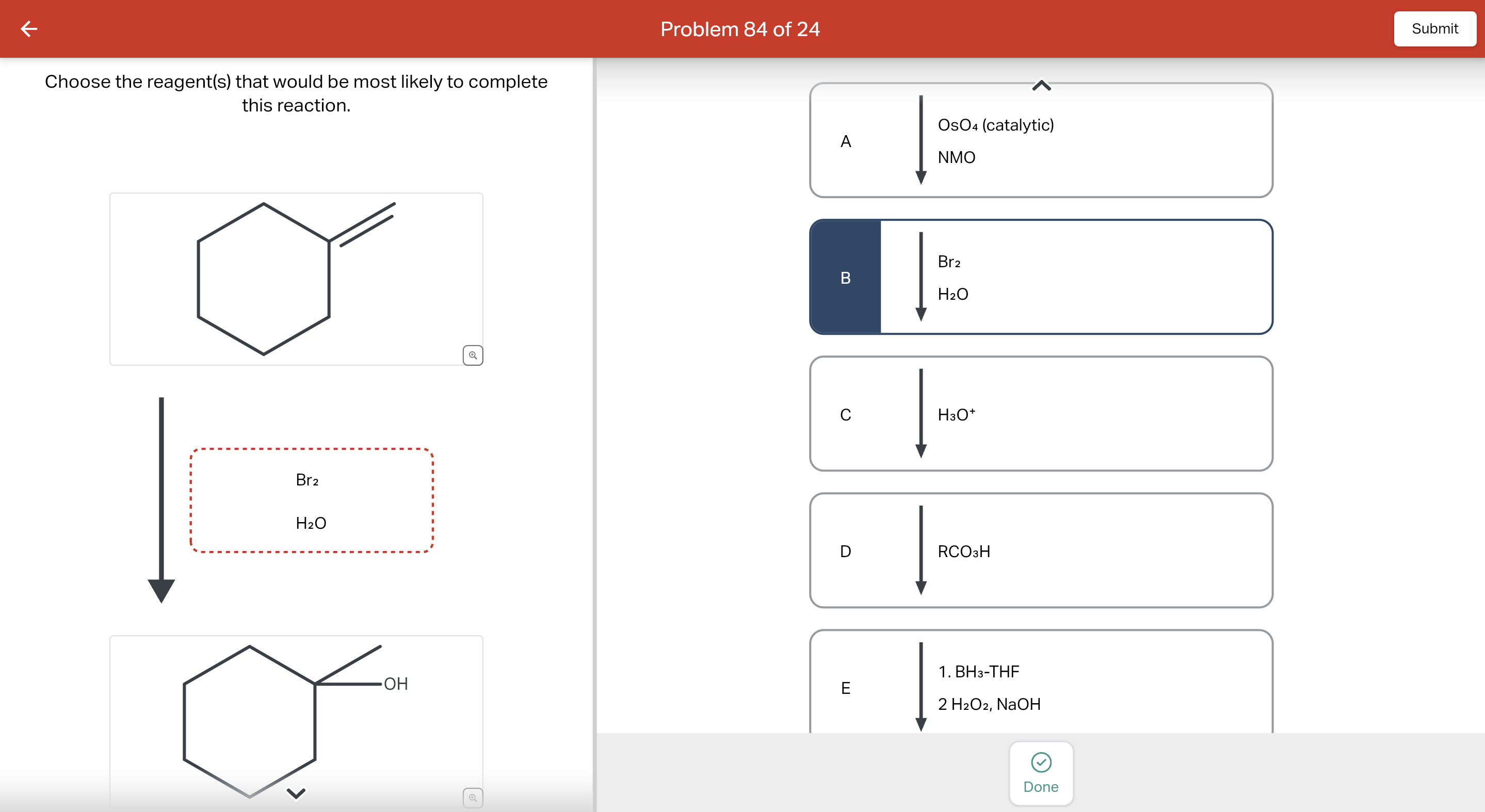
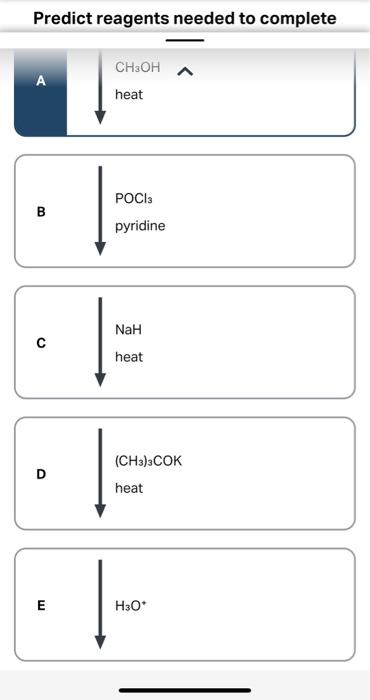
Question: Predict reagents needed to complete this E2 elimination reaction. Draw all elmination products that could be formed in this E2 reaction. Ignore any inorganic byproducts. Step 1. 1):-. We find the reagents which are used in the conversion reaction. The reactant molecule reacts with… View the full answer Step 2. Unlock.
Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
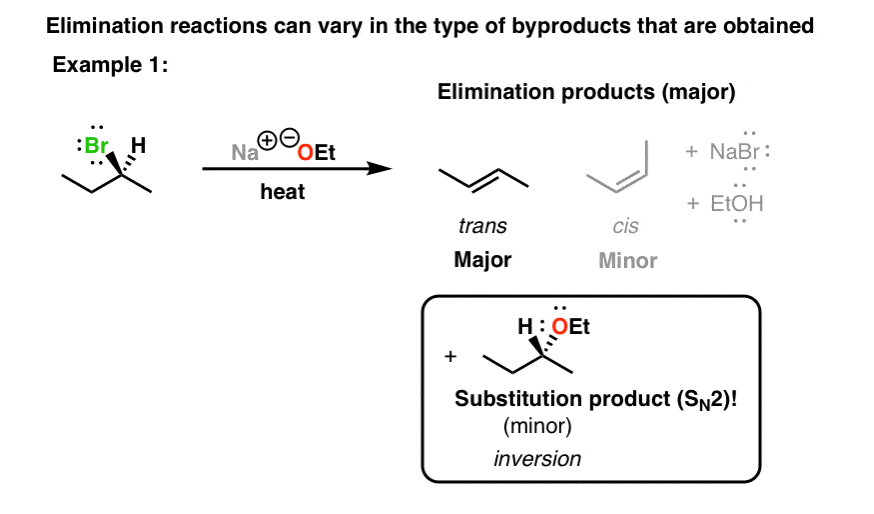
The key difference between the S N 2 and E2 reactions is that the nucleophile in the S N 2 mechanism attacks the carbon connected to the leaving group (ɑ-carbon) while in E2, the base attacks one of the β-hydrogens. The result is a replacement of the leaving group with a nucleophile, in the S N 2, and a newly-formed π bond in the E2 reaction.
Source Image: numerade.com
Download Image
Solved Starting from the wedge-and-dash structure below | Chegg.com When you look at the kinetics for an E2 mechanism, the overall rates of the reaction is equal to the rate constant times the concentration of the substrate to the first power, and the substrate is your alkyl halides, times the concentration of the base to the first power, so our strong base. And so, this is an elimination reaction that depends
Source Image: masterorganicchemistry.com
Download Image
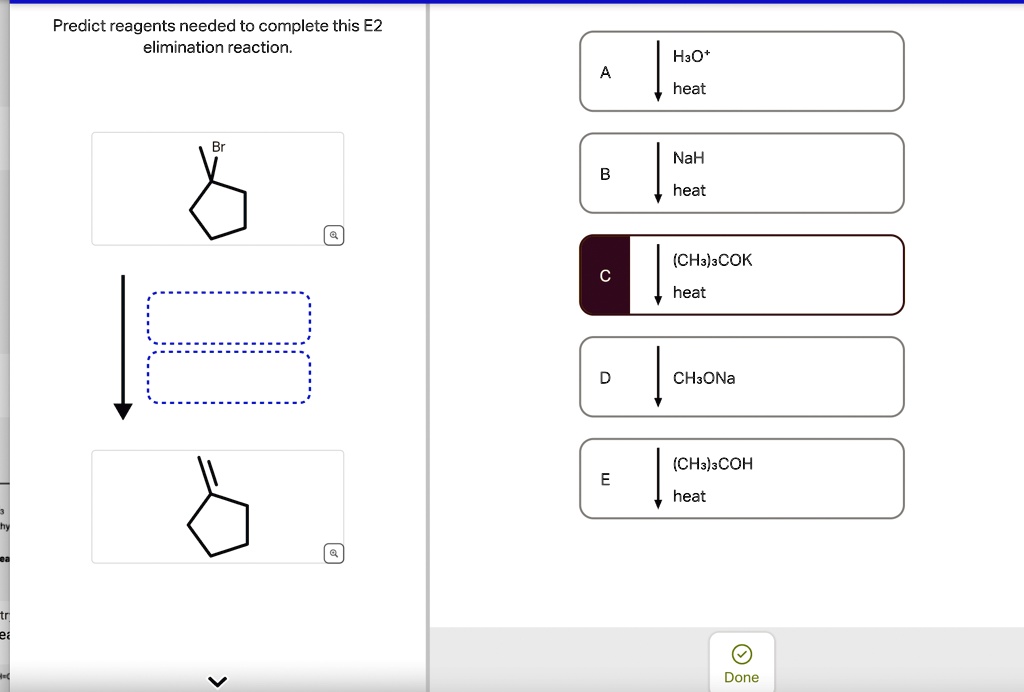
Predict Reagents Needed To Complete This E2 Elimination Reaction.
When you look at the kinetics for an E2 mechanism, the overall rates of the reaction is equal to the rate constant times the concentration of the substrate to the first power, and the substrate is your alkyl halides, times the concentration of the base to the first power, so our strong base. And so, this is an elimination reaction that depends By James Ashenhurst The E2 Mechanism Last updated: February 7th, 2023 | E2 Mechanism – How The E2 (Elimination, Biomolecular) Reaction Works Having gone through the E1 mechanism for elimination reactions, we’ve accounted for one way in which elimination reactions can occur.
Two Elimination Reaction Patterns – Master Organic Chemistry
Jan 23, 2023An overview of the E2 mechanism. At the beginning of this module, we saw the following reaction between tert-butyl bromide and cyanide. Clearly, this is not a substitution reaction. (3) (CH 3) 3 C – Br + CN (-) —— > (CH 3) 2 C =CH 2 + Br (-) + HCN We know that t-butyl bromide is not expected to react by an S N 2 mechanism. SOLVED: Predict reagents needed to complete this E2 elimination reaction. Br
Source Image: numerade.com
Download Image
Deciding SN1/SN2/E1/E2 (1) – The Substrate – Master Organic Chemistry Jan 23, 2023An overview of the E2 mechanism. At the beginning of this module, we saw the following reaction between tert-butyl bromide and cyanide. Clearly, this is not a substitution reaction. (3) (CH 3) 3 C – Br + CN (-) —— > (CH 3) 2 C =CH 2 + Br (-) + HCN We know that t-butyl bromide is not expected to react by an S N 2 mechanism.
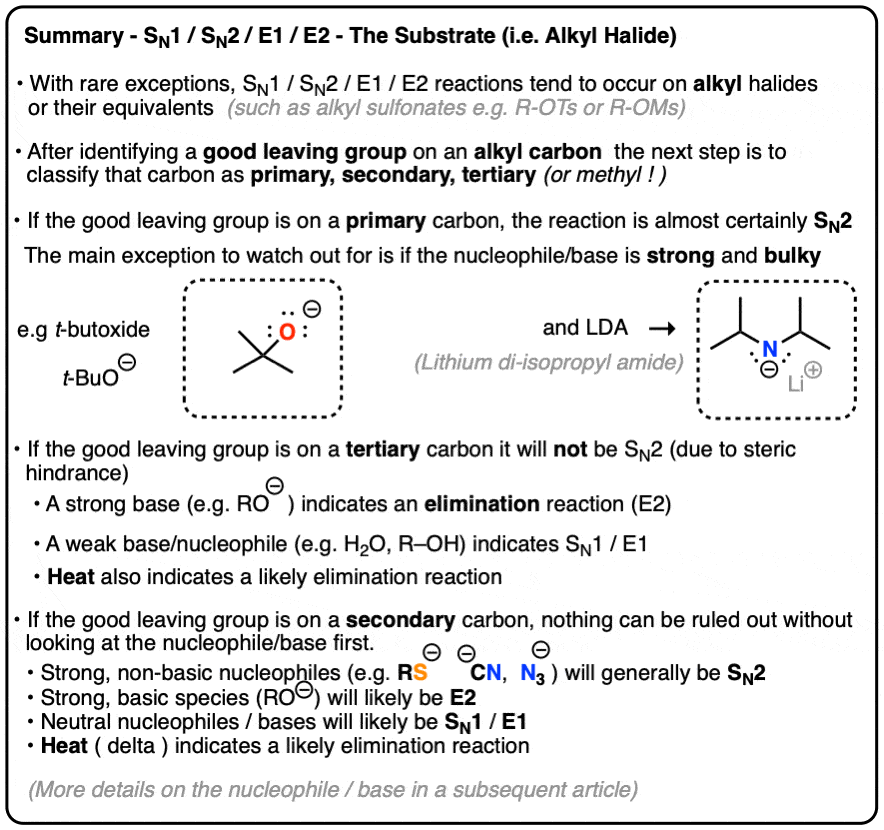
Source Image: masterorganicchemistry.com
Download Image
Answered: Predict reagents needed to complete… | bartleby 1. Identify the products and draw the curved-arrow mechanism for each of the following stereospecific E2 reaction: Drawing Newman projections to achieve the correct anti-periplanar conformation will be helpful. answer. This content is for registered users only.
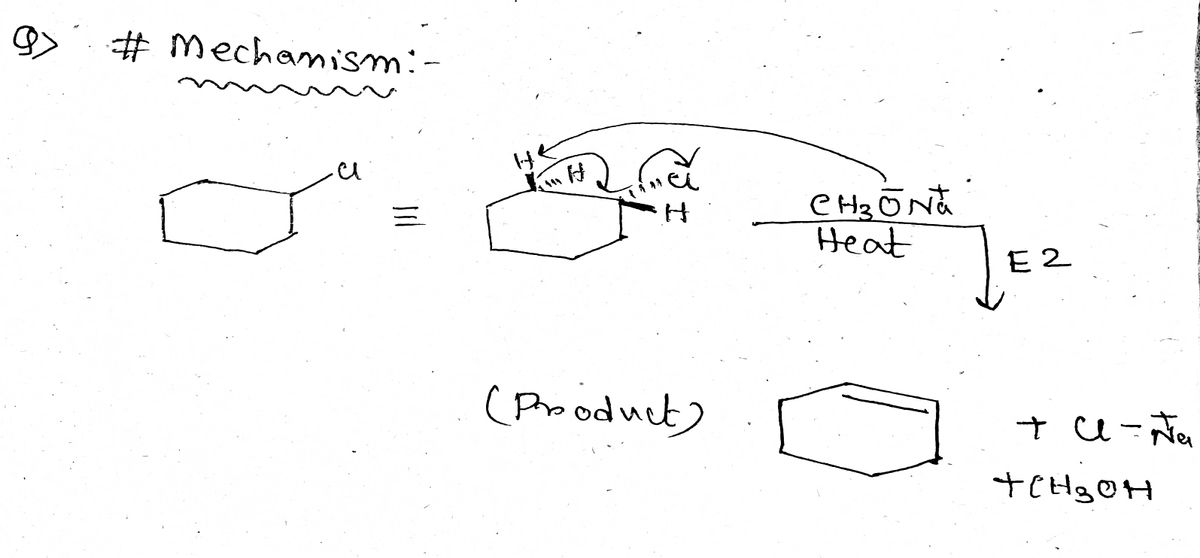
Source Image: bartleby.com
Download Image
Solved Starting from the wedge-and-dash structure below | Chegg.com The key difference between the S N 2 and E2 reactions is that the nucleophile in the S N 2 mechanism attacks the carbon connected to the leaving group (ɑ-carbon) while in E2, the base attacks one of the β-hydrogens. The result is a replacement of the leaving group with a nucleophile, in the S N 2, and a newly-formed π bond in the E2 reaction.
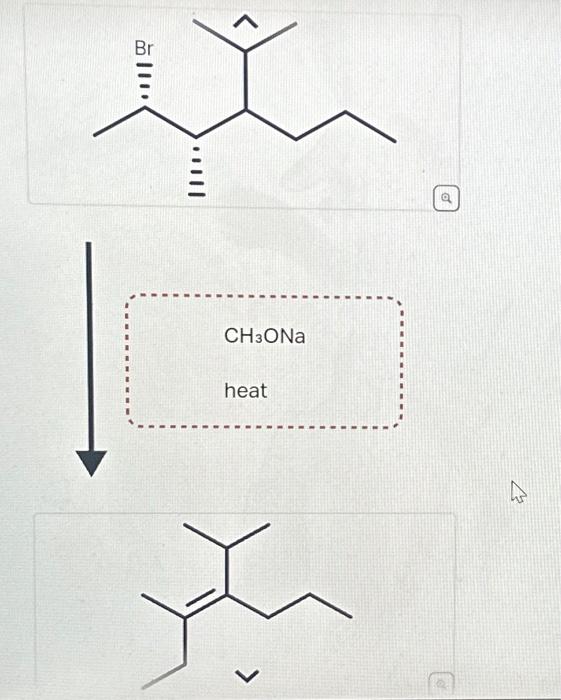
Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
Answered: Please predict the outcome of each E2… | bartleby Ernest Zinck. It is the nature of the α carbon that determines the type of substitution. If you have a 3° carbon, the substitution reaction will be SN1. For 1° and 2° carbons, the substitution will be SN2. It is the strength of the base that determines the type of elimination. If you have a strong base, you will get E2 elimination.
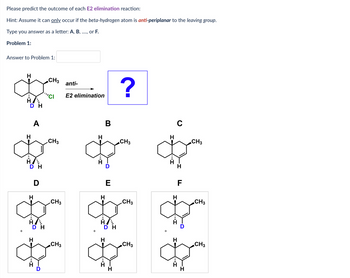
Source Image: bartleby.com
Download Image
8.5. Elimination reactions | Organic Chemistry 1: An open textbook When you look at the kinetics for an E2 mechanism, the overall rates of the reaction is equal to the rate constant times the concentration of the substrate to the first power, and the substrate is your alkyl halides, times the concentration of the base to the first power, so our strong base. And so, this is an elimination reaction that depends

Source Image: courses.lumenlearning.com
Download Image
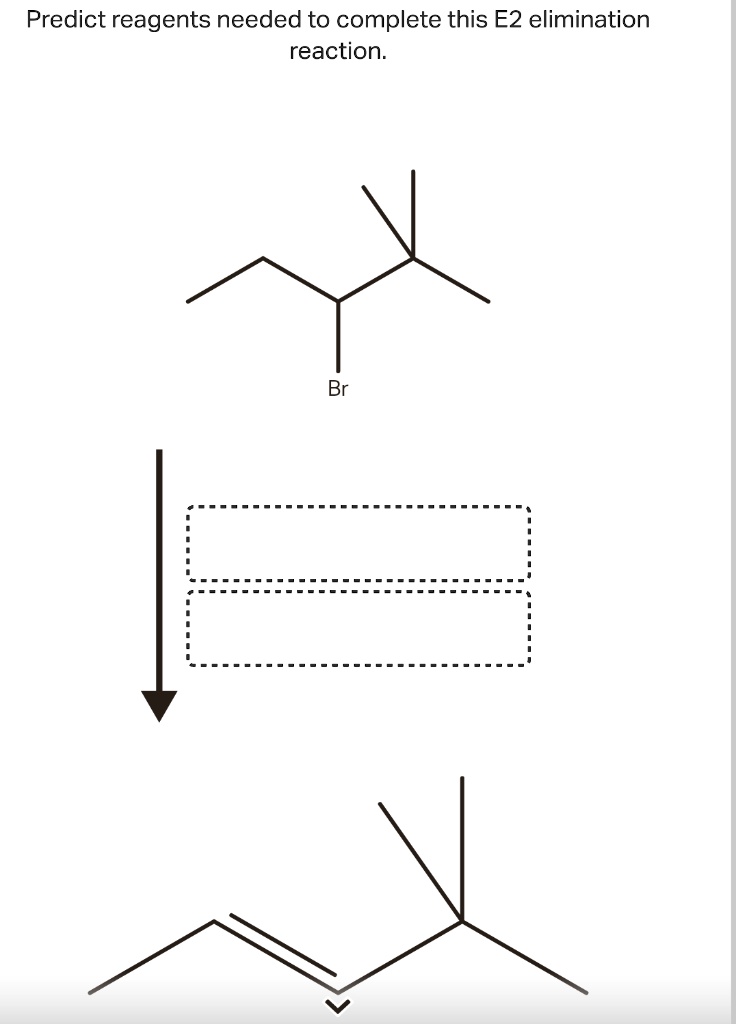
Solved Predict reagents needed to complete this E2 | Chegg.com By James Ashenhurst The E2 Mechanism Last updated: February 7th, 2023 | E2 Mechanism – How The E2 (Elimination, Biomolecular) Reaction Works Having gone through the E1 mechanism for elimination reactions, we’ve accounted for one way in which elimination reactions can occur.
Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
Deciding SN1/SN2/E1/E2 (1) – The Substrate – Master Organic Chemistry
Solved Predict reagents needed to complete this E2 | Chegg.com Question: Predict reagents needed to complete this E2 elimination reaction. Draw all elmination products that could be formed in this E2 reaction. Ignore any inorganic byproducts. Step 1. 1):-. We find the reagents which are used in the conversion reaction. The reactant molecule reacts with… View the full answer Step 2. Unlock.
Solved Starting from the wedge-and-dash structure below | Chegg.com 8.5. Elimination reactions | Organic Chemistry 1: An open textbook Ernest Zinck. It is the nature of the α carbon that determines the type of substitution. If you have a 3° carbon, the substitution reaction will be SN1. For 1° and 2° carbons, the substitution will be SN2. It is the strength of the base that determines the type of elimination. If you have a strong base, you will get E2 elimination.