Illustration of an activator. In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding to a specific DNA sequence. The function of TFs is to regulate—turn on and off—genes in order to make sure that they are expressed in the desired cells at
Central dogma of molecular biology – Wikipedia
The Transcription Factor Encyclopedia. Genome Biology 2012, 13:R24. … Following this exercise we are left with millions of gene to MeSH associations, and – in particular – 662,163 associations between TF-encoding genes and MeSH terms. Yet, not all associations are informative. For instance, the MeSH term ‘Humans’ is associated with many genes

Source Image: pubs.acs.org
Download Image
RNA polymerase, TFII factors. What are 2 upstream elements that serve as binding sites for transcription factors, to accelerate the rate at which RNA Polymerase binds to the promoter? enhancer, promoter proximal element. Transcription factors bind to this and facilitate binding of RNA Pol II: TATA BOX.

Source Image: khanacademy.org
Download Image
Cells | Free Full-Text | Regulation of Cell Cycle Progression by Growth Factor-Induced Cell Signaling Different kinds of cells have different patterns of transcription (known as gene expression). Gene expression also varies within a cell depending on the influence of external factors. View the animation below, then complete the quiz to test your knowledge of the concept. 1. DNA polymerase. RNA polymerase.

Source Image: keystoliteracy.com
Download Image
Which Of The Following Is True Of Transcription Factors
Different kinds of cells have different patterns of transcription (known as gene expression). Gene expression also varies within a cell depending on the influence of external factors. View the animation below, then complete the quiz to test your knowledge of the concept. 1. DNA polymerase. RNA polymerase. Which of the following statement(s) about basal transcription factors is(are) TRUE? A) they are essential for transcription: B) they cannot increase the rate of transcription by themselves: C) they can decrease the rate of transcription by themselves: D) A and B: E) A, B and C
Teaching Handwriting – Keys to Literacy
RNA polymerase is the molecule that makes mRNA. However it is not the only molecule needed for transcription. Other molecules recognize the site where transcription should start and create a complex that allows RNA polymerase to bind to the DNA and begin RNA synthesis. RNA polymerase does not have the ability to detect where it should start Genes | Free Full-Text | Transcription Factors That Govern Development and Disease: An Achilles Heel in Cancer
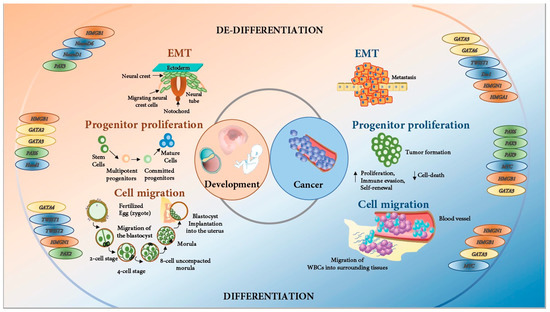
Source Image: mdpi.com
Download Image
An Approach to Derive Functional Peptide Inhibitors of Transcription Factor Activity | JACS Au RNA polymerase is the molecule that makes mRNA. However it is not the only molecule needed for transcription. Other molecules recognize the site where transcription should start and create a complex that allows RNA polymerase to bind to the DNA and begin RNA synthesis. RNA polymerase does not have the ability to detect where it should start

Source Image: pubs.acs.org
Download Image
Central dogma of molecular biology – Wikipedia Illustration of an activator. In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding to a specific DNA sequence. The function of TFs is to regulate—turn on and off—genes in order to make sure that they are expressed in the desired cells at

Source Image: en.wikipedia.org
Download Image
Cells | Free Full-Text | Regulation of Cell Cycle Progression by Growth Factor-Induced Cell Signaling RNA polymerase, TFII factors. What are 2 upstream elements that serve as binding sites for transcription factors, to accelerate the rate at which RNA Polymerase binds to the promoter? enhancer, promoter proximal element. Transcription factors bind to this and facilitate binding of RNA Pol II: TATA BOX.
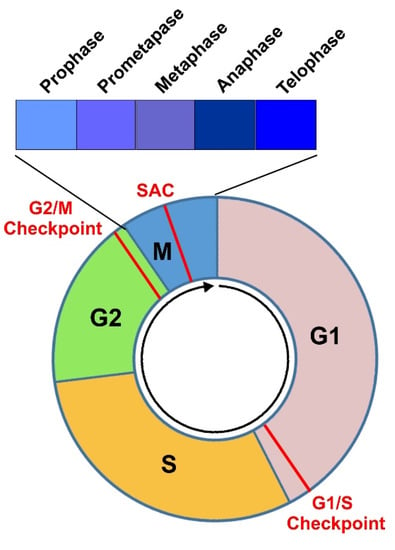
Source Image: mdpi.com
Download Image
Systematic Transfer of Prokaryotic Sensors and Circuits to Mammalian Cells | ACS Synthetic Biology Transcription Factor Definition. Transcription factors are DNA-binding proteins that play a key role in gene transcription. They are modular in structure and heterodimeric. Built within the transcription factor is a DNA-binding domain and several sites for the other transcription co-regulators to bind. Transcription factors bind to short

Source Image: pubs.acs.org
Download Image
6 of the Best Interview Transcription Software & Services (2024) Different kinds of cells have different patterns of transcription (known as gene expression). Gene expression also varies within a cell depending on the influence of external factors. View the animation below, then complete the quiz to test your knowledge of the concept. 1. DNA polymerase. RNA polymerase.
%20(1).webp)
Source Image: riverside.fm
Download Image
What does RNA polymerase do? | IDT Which of the following statement(s) about basal transcription factors is(are) TRUE? A) they are essential for transcription: B) they cannot increase the rate of transcription by themselves: C) they can decrease the rate of transcription by themselves: D) A and B: E) A, B and C

Source Image: idtdna.com
Download Image
An Approach to Derive Functional Peptide Inhibitors of Transcription Factor Activity | JACS Au
What does RNA polymerase do? | IDT The Transcription Factor Encyclopedia. Genome Biology 2012, 13:R24. … Following this exercise we are left with millions of gene to MeSH associations, and – in particular – 662,163 associations between TF-encoding genes and MeSH terms. Yet, not all associations are informative. For instance, the MeSH term ‘Humans’ is associated with many genes
Cells | Free Full-Text | Regulation of Cell Cycle Progression by Growth Factor-Induced Cell Signaling 6 of the Best Interview Transcription Software & Services (2024) Transcription Factor Definition. Transcription factors are DNA-binding proteins that play a key role in gene transcription. They are modular in structure and heterodimeric. Built within the transcription factor is a DNA-binding domain and several sites for the other transcription co-regulators to bind. Transcription factors bind to short